Research progress on the failure mechanism of ecological slope protection under multi-factor coupling in the Lower Yellow River
-
摘要:
黄河流域在中国经济社会发展中具有重要的战略地位,其下游河道水少沙多、水沙关系不协调,具有二级悬河、河势演变复杂等特点,岸坡破坏会严重威胁防洪安全和经济社会高质量发展,因此,保障岸坡稳定、开展黄河下游护坡治理与风险管控十分必要。生态护坡破坏涉及水、土、植被、结构等因素,机理复杂,传统河流动力学理论已不能完全适用,需进一步深入研究。本文总结分析了黄河下游岸坡破坏现状、岸坡失稳机理及其主要影响因素、生态护坡结构研究及应用和护坡工程风险评估及管控等方面现有研究成果及存在的不足,在此基础上探讨和梳理了黄河下游生态护坡未来的一些研究方向,包括揭示水-土-植被等多因素耦合作用下的生态护坡破坏机制、研发适用于强冲积特点的刚-柔协同新型生态护坡结构型式、建立考虑多要素多层次的生态护坡工程风险综合评价指标体系、形成岸坡监测-评估-处置/防护一体化的风险管控技术体系等。
Abstract:The Yellow River basin is of critical strategic importance to China's economic and social development. The lower reaches are characterized by low flow rates and high sediment concentrations, exhibiting an uncoordinated water-sediment relationship. This results in a secondary-perched river phenomenon and a complex evolution of river form. The degradation of bank slopes poses a significant threat to flood control integrity and hinders the economic and social development. Therefore, the preservation of riverbank stability and the implementation of effective slope protection and risk reduction measures are essential. The degradation of ecological slopes is a complex issue, influenced by a synergy of hydrological, pedological, vegetative, and structural stability elements, regulated by intricate processes. The inadequacies of current river dynamics theories necessitate in-depth investigation on this topic. This study compiled the current state of bank erosion in the lower Yellow River, elucidated the factors contributing to slope instability, and assessed the state-of-the-art in ecological slope protection methodologies and the challenges in risk evaluation and management protocols. The study identified key directions for future research in ecological slope protection, including: unraveling the degradation processes under hydro-soil-vegetation interactions; innovating rigid-flexible ecological slope protection structures adapted for intense alluvial conditions; developing comprehensive, tiered risk assessment models for ecological slope engineering; and constructing integrated frameworks for the monitoring, evaluation, and control of riverbank slope integrity.
-
黄河是中华民族的母亲河、中国第二大河流。黄河流域是中国重要的生态屏障和重要经济地带,在中国经济社会发展和生态安全方面具有十分重要的地位,黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展已上升为国家战略。黄河具有水沙异源、水少沙多、水沙关系不协调的特点[1],长期以来,黄土高原的大量泥沙进入下游河道,导致下游河床淤积抬升[2],形成“槽高、滩低、堤根洼”的“二级悬河”[3],使得黄河成为世界上最难治理的河流之一。黄河下游又是典型的强冲积性河流,河道面临冲刷加剧、畸形河湾发育等威胁防洪安全的问题[4]。此外,黄河流域生态相对脆弱,下游黄河三角洲区域易发生退化,恢复难度大且过程缓慢,使得黄河下游的系统治理更为不易。
为保障黄河安澜,人民治黄以来,先后对下游临黄大堤进行了4次加高培厚,总长为1 371 km,建成坝垛
5413 道、险工147处、控导工程233处,部分临水坡采用草皮护坡等技术,在保障黄河下游防洪安全和生态治理工作中发挥了显著作用。小浪底水库运行后,游荡段发生强烈冲刷,其断面持续趋向窄深,过流能力逐年恢复[5],但现状下游“二级悬河”依然严峻,叠加河势游荡的影响,(漫滩)洪水加剧对岸滩与堤防护坡的冲刷,易发生岸坡坍塌、滩地流失和护坡冲刷破坏,威胁滩区及沿河群众生命财产安全。如在2021年秋汛期,下游发生24段岸滩崩塌,长约10 km,205处工程不同程度出险。新情势下,保障黄河下游岸坡稳定,开展护坡治理与风险管控工作迫在眉睫。生态护坡已成为河道岸坡稳定防护的重要发展方向,是结合水利工程与生态环境保护而兴起的一种新型护坡技术[6]。植被是生态护坡的重要表现形式,也是河流良好生态功能的一项重要表征,可通过地下根系起到固滩护岸、稳定河势的作用[7-8]。在传统河道岸坡失稳研究中,河道中广泛存在的植被因子考虑相对较少,水流冲刷条件下考虑植被根系加筋锚固、护坡结构特性等作用的定量研究也相对较少;适用于黄河下游强冲积特点的生态护坡技术仍存在一定缺陷;现有生态护坡工程风险评价方法尚不成熟,指标体系不统一,评价等级划分差异较大;护坡工程风险管控技术有待完善。本文针对岸坡失稳机理及其主要影响因素、生态护坡结构研究及应用、护坡工程风险评估及管控等方面进行总结评述,针对现有研究不足提出研究展望,以期为黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展提供技术支撑。
1 岸坡失稳机理及其主要影响因素
1.1 研究区域概况及岸坡现状
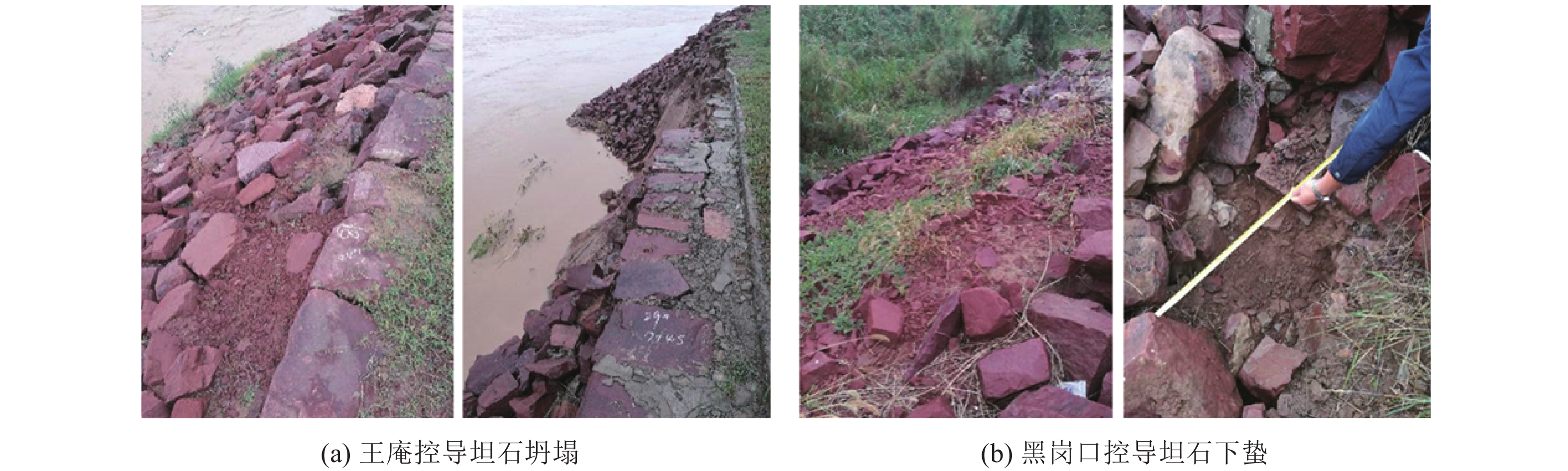
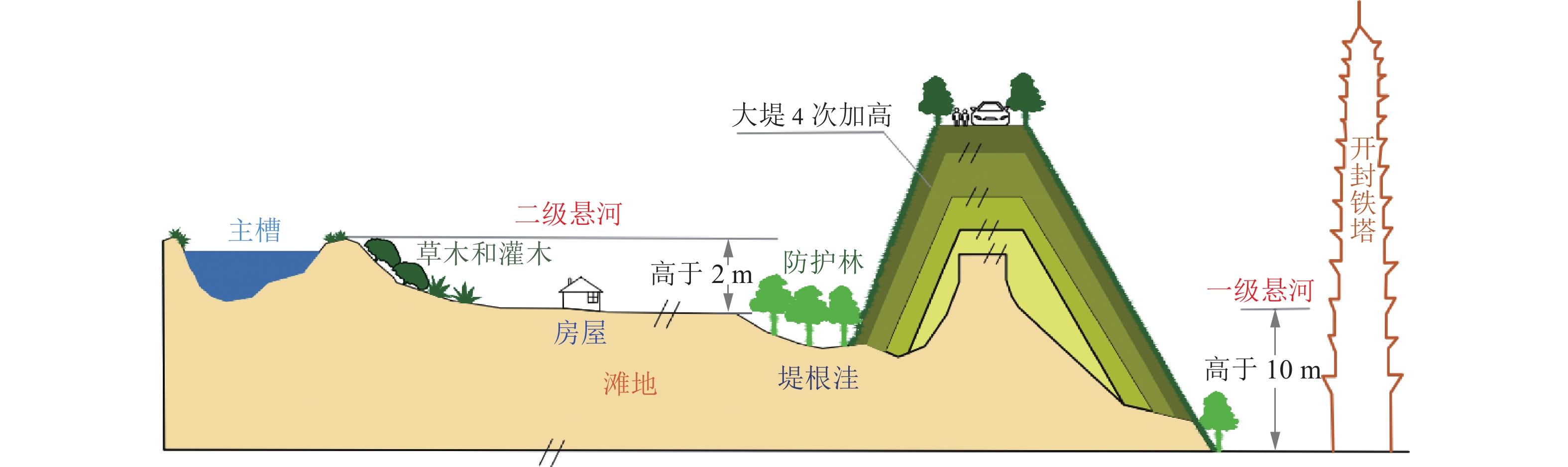
黄河下游从桃花峪以下至入海口,全长约786 km,河段落差为94 m,纵比降上陡下缓,平均约为1.2‱[9]。河道由主河槽与滩地共同构成,断面呈“宽滩窄槽”复式断面,滩槽关系复杂[10]。当前黄河下游水沙变化依然复杂[11],部分堤沟河仍未改观,局部河势演变剧烈[12],“二级悬河”严峻形势依然存在,如图1所示,岸坡冲刷仍是防洪安全和生态治理的重要威胁。据不完全统计,1985—2015年黄河下游河道工程重大险情次数超136次、较大险情超
1449 次,如表1所示。据1958—1996年几次大洪水堤防险情记载,其中85%的位置分布在距堤脚50 m内,14%分布在距堤脚50~100 m内[13];1999—2000年在对黄河下游671 km堤段隐患的调查中,发现较为明显的堤防隐患1330 处,裂缝向堤身延伸最长距离达13 m,裂缝下延深度达10 m[14];2006年汛期谢家闸断面左侧滩岸崩塌宽度达207.2 m;2018年汛期高水位时,长兴集断面坡脚淘刷,近岸河床最低点下降2.4 m[15];2018年以来黄河下游连续遭遇较大流量过程,特殊水沙条件致使韦滩控导工程靠河长度增长,主流形成向北的横流[16]。表 1 1985—2015年黄河下游河道工程险情统计Table 1 Statistics of dangerous situations in the Lower Yellow River channel engineering from 1985 to 2015时间 险情次数 抢险用石/万m3 重大 较大 一般 1985—1990年 33 143 4327 50.6 1991—1995年 13 88 3766 48.8 1996—2000年 35 428 5778 79.2 2001—2005年 28 455 12020 136.8 2006—2010年 17 174 5848 82.5 2011—2015年 10 161 5299 88.1 总计 136 1449 37038 486.0 1.2 水-土-植被等多因素耦合作用下护坡破坏机理
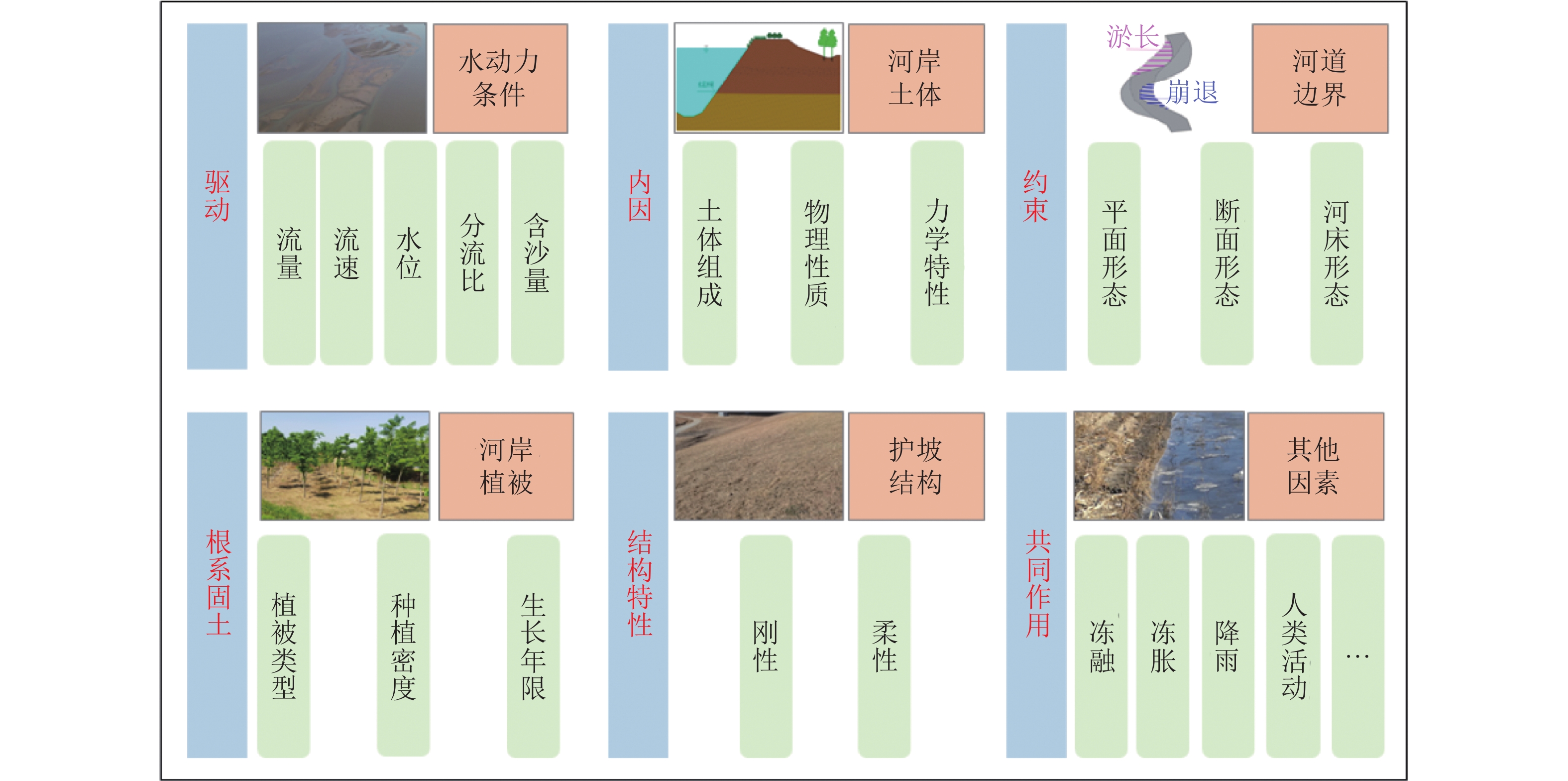
黄河下游水-土-植被耦合作用主要考虑水沙动力特征(流量、流速、含沙量等)、河道边界特征(河道形态、岸坡土体等)、护坡植被性能(根系加筋锚固、植被多样性等)三者之间的相互关系。水-土-植被耦合作用下影响护坡稳定的因素众多,既与水沙动力过程有关,又受到河道边界条件的影响,涉及水、土、植被、护坡结构等方面,机理十分复杂。
黄河水沙异源,近年来下游河床持续冲刷,床沙组成横向分布为主槽粗、滩地细,岸坡土体组成复杂,主要以砂壤土、壤土为主,局部混掺黏土、粉砂[17-19]。不同岸坡土体的冲刷失稳机理又有所不同。对非黏性土来说,在近岸水流的冲刷下,当岸坡水下坡角大于休止角时,岸坡将会失稳坍塌[20]。通常表现为单个颗粒的崩塌或移动,或沿微弯曲的浅层滑动面发生剪切破坏,以往研究中,从输沙平衡、土体守恒等角度,提出相应的非黏性岸滩崩塌计算模式[21-22]。对黏性土来说,当土体内部抗滑力小于滑动力时,岸坡将会发生失稳崩塌破坏。失稳破坏又分为剪切破坏和悬臂破坏[23],滑动力受到土体物理力学特性[24]等因素的影响。根据黏性土的崩岸机理,研究者们建立了相应的崩塌力学模式[25]。岸坡破坏机制可分为3个阶段:局部失稳阶段、扩张发展阶段和最终稳定阶段[26]。针对黄河下游复式二元或多元结构岸坡,当岸坡下部非黏性沙在水流的侵蚀淘刷下,其坡度接近休止角[27],上部黏土层悬臂,下部沙土冲刷将使悬臂土体失稳坍落。根据力学分析,学者们也推导建立相应的数学描述模式[28-29]。
黄河下游岸坡失稳影响因素众多,包括水动力条件[30]、植被分布[31]、河道边界地形[32]、水位[33-34]、土体特征[35]、护坡结构[36]和冻融冻胀[37]等方面,如图2所示。水动力作为主控因子,在岸滩崩塌过程中起着重要作用,包括含沙水流、糙率、主流冲刷、二次流淘刷以及渗流破坏等方面[38-41]。相同土质条件下,河床形态和河道演变也会影响岸坡失稳过程[42],如游荡段比弯曲段的崩岸变形要大[43]。土体特性对岸坡稳定存在显著影响[44],不同类型土体岸坡稳定性不同,土体应力分布对岸坡破坏起到关键作用[45];另外,受气候影响,冻融/冻胀会影响岸坡土体物理力学性质,进而影响岸坡稳定[46]。黄河下游河道两岸往往发育植被,可减少水流冲刷[47],植被根系又能稳定边坡,提高土壤的强度和韧性[48]。不同护坡结构作用不同,如混凝土防渗墙作为堤坝常用防渗结构[49],格宾网垫等柔性结构作为堤防加固技术[50],以提高堤防的抗冲性和稳定性。
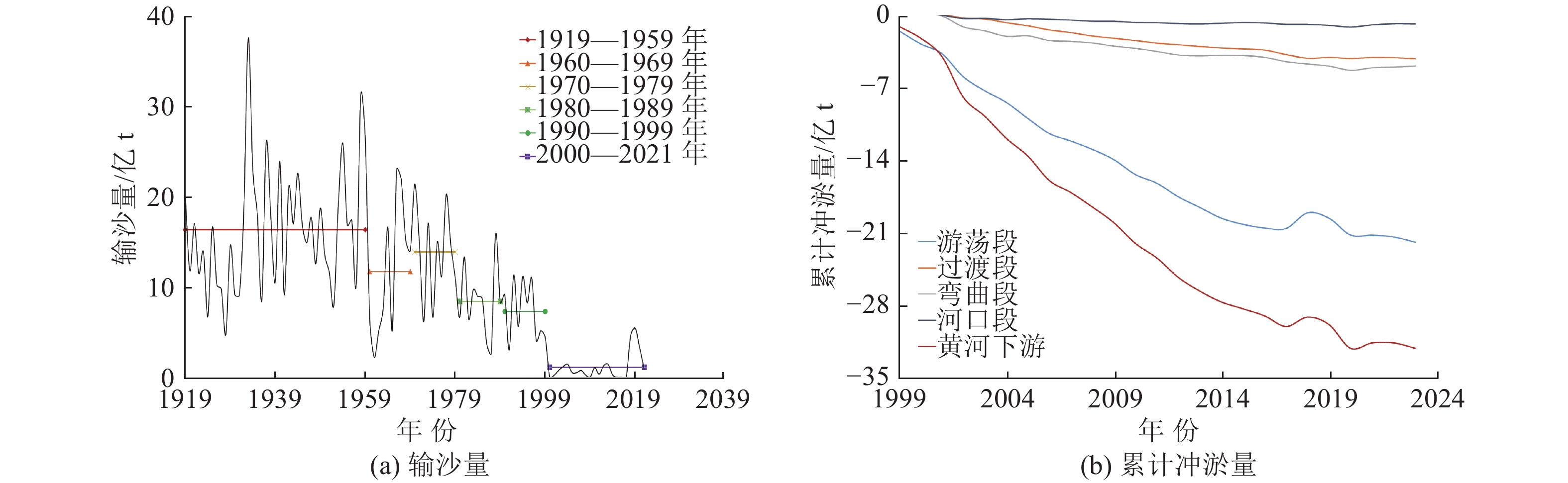
对黄河下游而言,水流冲刷是护坡破坏的重要因素,具体可表现为:黄河下游游荡性河段河势尚未完全控制,造成河势突变,使得险工段易冲刷出险;其特有的二级悬河形势,洪水一旦出槽,极易沿横比降集中归流,甚至直冲大堤;同时,由于“二级悬河”的存在,堤沟河往往长达数公里,容易顺堤行洪,产生顺堤的坡脚冲刷,造成护坡失稳。此外,黄河下游护坡破坏也受土体特性、来沙量、岸坡干湿变化等因素影响。土体特性方面,黄河下游岸坡以(砂)壤土为主,土体易冲易变形;另外下游年均来沙量减少,这些年尤其是小浪底运行以来[51],下游持续冲刷,冲刷量约32.15亿t,如图3所示。同时,由于上游水库调节作用,下游水位变化,导致岸坡土体干湿交替,也会降低岸坡稳定性。
总体而言,现有研究较少深入将根系作用机理与模式用于冲积河流岸滩稳定计算中[52],结合黄河下游二级悬河、河势演变复杂等特点,进一步考虑与不同生态护坡结构类型组合影响的定量研究亦相对较少,尚不能完全回答水流冲刷下水-土-植被等多因素耦合作用对护坡稳定破坏机制这一科学问题。
2 生态护坡结构研究及应用
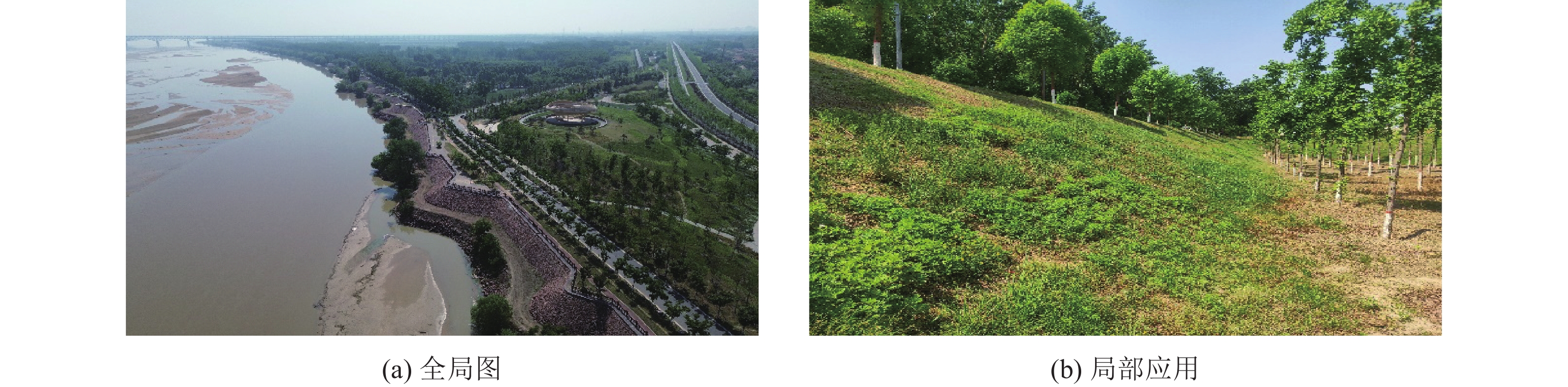
植被是黄河流域复杂人地耦合系统中的关键因子[53],起到防洪固土、减少土壤侵蚀的作用[54],也是拦蓄洪灾的重要手段[55]。目前,植被护坡在黄河下游应用较多,植被根系可增加岸坡稳定性[56],植被也可对河流系统生态功能的保护与修复起到重要作用。植被护岸常以乔灌结合的形式为主,选用高大乔木、低矮灌木及其他花草,与近岸河水共同组成一个立体的生态系统[57]。结合黄河下游流域特点,典型植被有芦苇、柽柳等[58],使用狗牙根、狗尾草等[59]防洪固土效果亦较好。图4为黄河下游马渡段典型生态护坡情况。
自20世纪70年代开始,黄河下游进行了一系列的新结构、新材料、新技术的试验,但现有生态护坡效果仍受到施工技术、质量控制方式以及外部环境等因素的影响,明确工程结构、植被、固化黄土一体化的综合生态护坡技术是边坡防护的必然趋势[60]。黄河不同区域在综合生态保护和工程稳定性等方面已开展了护坡结构的应用研究,例如,黄土边坡陕西段前期使用黑麦草边坡,后应用新型边坡防护材料聚丙烯纤维,并改为加筋黄土防护,采用快速植生的多功能层设计等方法解决边坡上植被生长缓慢等问题[61];黄河下游济南段在靠水几率较高的堤段采用狗牙根+三维网方案进行防护[62];济南段左岸赵庄险工处,护坡采用格构梁结构摊铺植生混凝土并播种狗牙根,坡脚用浆砌石[63];利津东坝控导工程处,抢险时采用抛投扭王(工)体混凝土+大块石+铅丝笼组合,达到1+1+1>3的效果[64];菏泽段的整治工程为提高坡脚的稳定性,在重点受溜容易出险的部位抛大块石、铅丝笼、混凝土四角锥体[65];下游左岸小开河引黄灌区,护坡选用联锁式护坡水工砖衬砌,并提出现浇混凝土衬砌适用于地上渠,浆砌石衬砌适用于石材丰富、价格较低的情况[66];下游原阳仁村堤护滩工程采用土工枕布护坡[67],等。
上述护坡工程技术应用取得了很好的成果,但仍存在护坡结构耐久性不足、生态护坡型式单一[68]等问题。由于黄河下游存在岸坡土质结构较为松散等特点,易出现不均匀沉陷等问题,且现有应用大多未深入考虑黄河下游河道的强冲积特点。此外,现有研究针对生态护岸稳定性的定量化评价考虑因素相对单一,从多学科交叉融合出发,综合考虑水、土、植被等因素耦合作用,其生态护坡结构仍需进一步优化。
3 护坡工程风险评估及管控
护坡工程失稳破坏危害巨大,威胁堤防安全和群众生命财产安全。建立护坡工程风险评价指标体系,识别相应主控判别指标及其维持稳定的阈值范围,是实现护坡工程风险管控的关键基础。
3.1 岸坡破坏风险评估研究方法
从不同角度和方法出发,岸坡破坏风险评估研究方法主要包括传统的经验法、力平衡分析法、岸坡稳定性综合判断法。基于经验方法的岸坡破坏风险评估以河床演变分析原理为基础,构建岸坡破坏特征参数(包括岸坡高度、护岸工程损毁情况、岸坡破坏崩塌速率及累计崩塌宽度等)与水沙边界条件及岸坡边界条件等特征参数(如近岸水深、平滩流量、水流冲刷强度、岸坡形态等)之间的关系[69-70]。如Rosgen[69]提出的经验方法以岸坡侵蚀危险指标和近岸水流切应力指标为独立变量,构建了破坏后退速率与这2个指标之间的经验关系,其中,岸坡侵蚀危险指标以岸坡高度/平滩水深、护岸工程覆盖度、植被根系长度/岸坡高度、根系密度等指标为依据,该方法被相关研究者所广泛采用[71-72]。但由于不同河流水文及地貌特征的差异,经验法的适用性相对有限。
基于力平衡分析方法,有关学者以临界崩塌高度[73]、临界挂空长度[74]等作为判别指标,同时引入土力学边坡安全系数的概念,构建岸坡破坏风险评估模型。在此基础上,耦合水沙输移、床面冲淤计算等模块,建立基于动力学过程的岸坡模拟技术,从而实现岸坡破坏过程模拟。断面尺度及一维尺度的岸坡稳定性模型分别以美国国家泥沙实验室开发的BSTEM和CONCEPTS模型为代表,广泛应用于科学研究和工程设计[75-76]。通过局部网格可动技术,将断面尺度模型与二维或三维水沙数学模型耦合,在岸坡稳定性研究方面取得了很好的成果[77-78]。但二维、三维的数学模型通常对岸坡破坏过程进行了简化,且通常多适用于天然未护岸坡的模拟,一定程度上限制了模型在实际护坡工程中的应用。
岸坡稳定性影响因素众多,各因素之间存在复杂的非线性关系,现阶段岸坡破坏机理难以建立多因素耦合作用下的力学模式。通过对不同类型岸坡破坏主要影响因素进行权重赋值,可以对岸坡稳定性进行综合评估;将模糊评价法和层次分析方法相结合,利用层次分析法确定各指标的权重,用模糊评价法对数据进行评估[79];亦可利用概率评估等模型定义河岸破坏风险[80]。
3.2 护坡工程风险管控研究
护坡工程风险管控包括监测、评估、处置、防护以及高效管理等多个方面。中国在治河实践中,针对长江、黄河等大江大河的护坡工程风险管控方面积累了较丰富的经验,并取得了一些技术性突破[81]。
针对护坡工程风险监测方面,利用无人机倾斜摄影技术,考虑监测点的动态性质,可实现护坡损害监测[82],或采用边坡多场监测的新型光纤传感器[83],但面对黄河下游随机、复杂的岸坡破坏过程,还应建立长期观测机制[84]。护坡工程风险评价方面,上文有经验法、力平衡分析法、岸坡稳定性综合判断法等方法。针对护坡工程风险处置方面,可采用格宾石笼护坡、抛石护脚[85]等措施。护坡工程防护方面,在工程型式上,由传统的守点工程(包括丁坝、矶头等)改进为平顺型护岸。在护岸材料上,随着研究的不断深入,先后采用了柴枕、混凝土铰链排、抛石、塑护软体排混凝土异形块、四面六边透水框架和钢丝石笼护岸[86-87]。基于护岸工程结构安全、资源节约、生态修复等多因素需求,研发了网模卵石排、网筋人工石群等水新型下护岸工程技术[88]。针对护坡工程管理方面,中国江河护坡工程治理以防洪为主,通常关注工程构造安全性及耐久性。随着回归自然、生态环保、亲水景观等理念的深入人心,生态型护岸理念应运而生[89],加筋生态护坡技术作为一项兼顾强度和生态的新兴技术得到广泛应用[90]。在治理边坡生态保护问题时,根据植被生长特性要求,改进或研发植物生长基质[91]。目前,抛投防汛石是黄河河道整治、抢险救灾的主要手段[92]。
经过不断探索与发展,护坡工程技术已在实践中积累了较丰富的经验,生态护坡被越来越广泛应用于江河湖海、城市及流域治理等各类护坡工程中。但护坡工程风险管控涉及内容多,护坡破坏仍然多发(图5),除了防护处置外,还涉及监测、评估以及管控等多方面,需要进一步开展一体化的研究,从而实现护坡工程事前预防(监测)与高效管控。
4 结论及展望
生态护坡已成为河道岸坡防护发展的重要方向,生态护坡稳定受自然与人类活动共同作用,影响因素多,且伴随水力侵蚀、岸坡土体破坏、植被根系固土等多个动力过程,在黄河下游特殊的水沙条件下机理更加复杂,需要采用河流动力学、土力学、植被学、结构力学等多学科交叉理论来开展研究。
(1)当前对不同类型土体岸坡失稳过程、机理及其力学模式方面,已开展了较为深入的研究工作,但主要考虑水动力条件、岸坡土体特性等因素,尚未深入考虑水流冲刷条件下植被根系固土作用、护坡结构特性等因素的耦合作用。未来还需深入研究水-土-植被耦合作用下黄河下游主槽岸滩与堤防护坡的破坏机理,丰富多因素耦合作用下生态护坡稳定机制的理论研究,并建立相应的数学描述模式。
(2)生态护坡工程研究与应用已取得了较好进展,但在黄河下游“二级悬河”和河势演变复杂的背景下,如何针对其强冲积特点,考虑水流冲刷、植被根系固土效应(加筋、锚固)等因素,建立水流冲刷作用下生态护坡稳定性的模拟方法,提出刚-柔协同新型生态护坡结构,并确定利于提升岸坡稳定性的植被优选布置形式,在保障护坡结构安全、岸坡稳定的基础上,实现岸坡生态化和景观美化。
(3)针对岸坡(稳定)风险评价,当前采用传统的经验评估法、力平衡分析法、岸坡稳定性综合判断评估法等已开展了较为深入的研究工作,但受生态护坡破坏影响因素众多的限制,生态护坡工程风险综合评价指标体系仍需深入研究。如何在河势、水、沙、土、植被、护坡结构型式等众多因素中,识别生态护坡工程风险的主控指标,确定各指标维持岸坡稳定的阈值范围,建立考虑多要素多层次的生态护坡工程风险综合评价指标体系,实现对破坏可能性、危害程度以及风险等级的综合评价,仍是当前亟需研究的重要问题。
(4)生态护坡工程处置和防护技术取得了较好进展,但受生态护坡工程破坏机制认识不深和风险综合评价指标体系不完善的限制,其风险管控技术还有待进一步研究。如何基于水-土-植被等多因素耦合作用生态护坡破坏机理和风险综合评价指标体系,提出岸坡监测-评估-处置/防护一体化的风险管控技术体系,实现岸坡破坏事前预防,也是实现黄河下游生态护坡工程高效管控的一项关键所在。
鉴于黄河下游河道仍将长期处于动态调整中及其特殊水沙条件,未来研究方向可以黄河下游生态护坡破坏机制研究为基础,研发适用强冲积特点的刚-柔协同新型生态护坡结构型式,结合风险综合评价指标体系综合提出生态护坡风险管控技术。既关注黄河下游生态护坡破坏机理与防护治理的共性问题,同时又要对重点河段开展生态护坡风险评估和风险管控技术研发。
-
表 1 1985—2015年黄河下游河道工程险情统计
Table 1 Statistics of dangerous situations in the Lower Yellow River channel engineering from 1985 to 2015
时间 险情次数 抢险用石/万m3 重大 较大 一般 1985—1990年 33 143 4327 50.6 1991—1995年 13 88 3766 48.8 1996—2000年 35 428 5778 79.2 2001—2005年 28 455 12020 136.8 2006—2010年 17 174 5848 82.5 2011—2015年 10 161 5299 88.1 总计 136 1449 37038 486.0 -
[1] 张红武,方红卫,钟德钰,等. 宁蒙黄河治理对策[J]. 水利水电技术,2020,51(2):1-25. (ZHANG H W,FANG H W,ZHONG D Y,et al. Control measurements in Ningmeng reach of the Yellow River[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2020,51(2):1-25. (in Chinese) ZHANG H W, FANG H W, ZHONG D Y, et al. Control measurements in Ningmeng reach of the Yellow River[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2020, 51(2): 1-25. (in Chinese)
[2] 张金良,刘生云,李超群. 论黄河下游河道的生态安全屏障作用[J]. 人民黄河,2018,40(2):21-24. (ZHANG J L,LIU S Y,LI C Q. Discussion on effect of ecological security barrier of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River,2018,40(2):21-24. (in Chinese) ZHANG J L, LIU S Y, LI C Q. Discussion on effect of ecological security barrier of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River, 2018, 40(2): 21-24. (in Chinese)
[3] 左其亭,邱曦,马军霞,等. 黄河治水思想演变及现代治水方略[J]. 水资源与水工程学报,2023,34(3):1-9. (ZUO Q T,QIU X,MA J X,et al. Evolution of flood control thought and modern flood control strategy in the Yellow River basin[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering,2023,34(3):1-9. (in Chinese) ZUO Q T, QIU X, MA J X, et al. Evolution of flood control thought and modern flood control strategy in the Yellow River basin[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2023, 34(3): 1-9. (in Chinese)
[4] 胡春宏,张治昊,张晓明. 维持黄河流域水沙平衡的调控指标阈值体系研究[J]. 水科学进展,2023,34(5):647-659. (HU C H,ZHANG Z H,ZHANG X M. Threshold system of regulation indicators for maintaining the runoff and sediment balance of the Yellow River basin[J]. Advances in Water Science,2023,34(5):647-659. (in Chinese) HU C H, ZHANG Z H, ZHANG X M. Threshold system of regulation indicators for maintaining the runoff and sediment balance of the Yellow River basin[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2023, 34(5): 647-659. (in Chinese)
[5] 程亦菲,夏军强,周美蓉,等. 黄河下游游荡段过流能力调整对水沙条件与断面形态的响应[J]. 水科学进展,2020,31(3):337-347. (CHENG Y F,XIA J Q,ZHOU M R,et al. Response of flood discharge capacity to the incoming flow and sediment regime and channel geometry in the braided reach of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science,2020,31(3):337-347. (in Chinese) CHENG Y F, XIA J Q, ZHOU M R, et al. Response of flood discharge capacity to the incoming flow and sediment regime and channel geometry in the braided reach of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2020, 31(3): 337-347. (in Chinese)
[6] 曾贺,谌奔波,张晓华. 黄河下游生态护坡构建研究[J]. 人民黄河,2010,32(2):23-24. (ZENG H,CHEN B B,ZHANG X H. Study on establishment of ecological slope protection of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River,2010,32(2):23-24. (in Chinese) ZENG H, CHEN B B, ZHANG X H. Study on establishment of ecological slope protection of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River, 2010, 32(2): 23-24. (in Chinese)
[7] EMADI-TAFTI M,ATAIE-ASHTIANI B,HOSSEINI S M. Integrated impacts of vegetation and soil type on slope stability:a case study of Kheyrud Forest,Iran[J]. Ecological Modelling,2021,446:109498. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2021.109498
[8] HUAI W X,LI S L,KATUL G G,et al. Flow dynamics and sediment transport in vegetated rivers:a review[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics,2021,33(3):400-420. doi: 10.1007/s42241-021-0043-7
[9] 曹玉芹,夏军强,周美蓉,等. 汛期与非汛期水沙条件对黄河下游不同河段过流能力的影响[J]. 水科学进展,2024,35(4):617-628. (CAO Y Q,XIA J Q,ZHOU M R,et al. Effects of flood and non-flood flow and sediment regimes on the flood discharge capacity of different reaches in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science,2024,35(4):617-628. (in Chinese) CAO Y Q, XIA J Q, ZHOU M R, et al. Effects of flood and non-flood flow and sediment regimes on the flood discharge capacity of different reaches in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2024, 35(4): 617-628. (in Chinese)
[10] 江恩慧,屈博,王远见,等. 基于流域系统科学的黄河下游河道系统治理研究[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版),2021,42(4):7-15. (JIANG E H,QU B,WANG Y J,et al. Research on synergistic regulation of the Lower Yellow River based on watershed system science[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power(Natural Science Edition),2021,42(4):7-15. (in Chinese) JIANG E H, QU B, WANG Y J, et al. Research on synergistic regulation of the Lower Yellow River based on watershed system science[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 42(4): 7-15. (in Chinese)
[11] 景唤,钟德钰,张红武,等. 中小流量下黄河下游游荡段河床调整规律[J]. 水力发电学报,2020,39(4):33-45. (JING H,ZHONG D Y,ZHANG H W,et al. Riverbed adjustment characteristics in braided reaches of Lower Yellow River under small and medium discharges[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering,2020,39(4):33-45. (in Chinese) JING H, ZHONG D Y, ZHANG H W, et al. Riverbed adjustment characteristics in braided reaches of Lower Yellow River under small and medium discharges[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2020, 39(4): 33-45. (in Chinese)
[12] 张原锋,王平. 黄河下游游荡型河段床面形态变化特征[J]. 人民黄河,2018,40(8):8-11. (ZHANG Y F,WANG P. Variation characteristics of bedforms in wandering reach of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River,2018,40(8):8-11. (in Chinese) ZHANG Y F, WANG P. Variation characteristics of bedforms in wandering reach of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River, 2018, 40(8): 8-11. (in Chinese)
[13] 郭全明,张宝森,仵海英. 黄河堤防险情调查分析[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2003,14(3):45-49. (GUO Q M,ZHANG B S,WU H Y. Investigation and analysis of risk of dike of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2003,14(3):45-49. (in Chinese) GUO Q M, ZHANG B S, WU H Y. Investigation and analysis of risk of dike of the Yellow River[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2003, 14(3): 45-49. (in Chinese)
[14] 张秀勇. 黄河下游堤防破坏机理与安全评价方法的研究[D]. 南京:河海大学,2005. (ZHANG X Y. Study on failure mechanism and safety evaluation method of dikes in the lower reaches of the Yellow River[D]. Nanjing:Hohai University,2005. (in Chinese) ZHANG X Y. Study on failure mechanism and safety evaluation method of dikes in the lower reaches of the Yellow River[D]. Nanjing: Hohai University, 2005. (in Chinese)
[15] 高璐,彭秀竹,李依杭,等. 黄河下游典型河段滩岸崩退特性研究[J]. 人民黄河,2024,46(2):49-54,66. (GAO L,PENG X Z,LI Y H,et al. Study on characteristics of riverbank collapse in typical section of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River,2024,46(2):49-54,66. (in Chinese) GAO L, PENG X Z, LI Y H, et al. Study on characteristics of riverbank collapse in typical section of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River, 2024, 46(2): 49-54, 66. (in Chinese)
[16] 张春晋,张敏,姚文艺,等. 黄河下游三官庙至韦滩河段主流摆动规律及其驱动机制[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,2023,31(5):1110-1124. (ZHANG C J,ZHANG M,YAO W Y,et al. Mainstream swing rule and its driving mechanism in the Sanguanmiao to Weitan reach of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,2023,31(5):1110-1124. (in Chinese) ZHANG C J, ZHANG M, YAO W Y, et al. Mainstream swing rule and its driving mechanism in the Sanguanmiao to Weitan reach of the Lower Yellow River[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2023, 31(5): 1110-1124. (in Chinese)
[17] 胡春宏,张晓明,赵阳. 黄河泥沙百年演变特征与近期波动变化成因解析[J]. 水科学进展,2020,31(5):725-733. (HU C H,ZHANG X M,ZHAO Y. Cause analysis of the centennial trend and recent fluctuation of the Yellow River sediment load[J]. Advances in Water Science,2020,31(5):725-733. (in Chinese) HU C H, ZHANG X M, ZHAO Y. Cause analysis of the centennial trend and recent fluctuation of the Yellow River sediment load[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2020, 31(5): 725-733. (in Chinese)
[18] 夏军强,刘鑫,张晓雷,等. 黄河下游动床阻力变化及其计算方法[J]. 水科学进展,2021,32(2):218-229. (XIA J Q,LIU X,ZHANG X L,et al. Variation characteristics and formula of movable bed roughness for the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science,2021,32(2):218-229. (in Chinese) XIA J Q, LIU X, ZHANG X L, et al. Variation characteristics and formula of movable bed roughness for the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2021, 32(2): 218-229. (in Chinese)
[19] 申冠卿,张原锋,王平,等. 水库拦沙对黄河下游河床演变的影响[J]. 水科学进展,2024,35(3):475-484. (SHEN G Q,ZHANG Y F,WANG P,et al. Impact of sediment retention by reservoirs on the fluvial process in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science,2024,35(3):475-484. (in Chinese) SHEN G Q, ZHANG Y F, WANG P, et al. Impact of sediment retention by reservoirs on the fluvial process in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2024, 35(3): 475-484. (in Chinese)
[20] IKEDA S,PARKER G,KIMURA Y. Stable width and depth of straight gravel rivers with heterogeneous bed materials[J]. Water Resources Research,1988,24(5):713-722. doi: 10.1029/WR024i005p00713
[21] HAO Y Z,JIA D D,ZHANG X N,et al. Stability analysis of riverbanks with a dual structure under water-root-soil coupling[J]. Water Science and Technology:Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research,2023,88(3):658-676. doi: 10.2166/wst.2023.225
[22] XU D D,LU B,CHENG Y H,et al. A continuous-discontinuous deformation analysis method for simulating the progressive failure process of riverbanks[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements,2022,143:137-151. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2022.06.012
[23] PATSINGHASANEE S,KIMURA I,SHIMIZU Y,et al. Coupled studies of fluvial erosion and cantilever failure for cohesive riverbanks:case studies in the experimental flumes and U-Tapao River[J]. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research,2017,16:13-26.
[24] ZHANG H K,LI C D,YAO W M,et al. A novel approach for determining pile spacing considering interactions among multilayered sliding masses in colluvial landslides[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2019,23(9):3935-3950. doi: 10.1007/s12205-019-0459-6
[25] 王延贵,陈吟,陈康. 冲积河流岸滩崩退模式与崩退速率[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2018,38(4):14-20. (WANG Y G,CHEN Y,CHEN K. Study on collapse-retreat patterns and bank erosion rates of alluvial riverbanks[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources,2018,38(4):14-20. (in Chinese) WANG Y G, CHEN Y, CHEN K. Study on collapse-retreat patterns and bank erosion rates of alluvial riverbanks[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2018, 38(4): 14-20. (in Chinese)
[26] ZHAO J J,ZHANG H Y,YANG C X,et al. Experimental study of reservoir bank collapse in gravel soil under different slope gradients and water levels[J]. Natural Hazards,2020,102(1):249-273. doi: 10.1007/s11069-020-03922-z
[27] CHEN D,DUAN J G. Case study:two-dimensional model simulation of channel migration processes in West Jordan River,Utah[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2008,134(3):315-327. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2008)134:3(315)
[28] LANGENDOEN E J,SIMON A. Modeling the evolution of incised streams:II:streambank erosion[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2008,134(7):905-915. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2008)134:7(905)
[29] CHEN F,WANG Y C,LI Y H,et al. Investigation on the collapse mechanism of overlying clay layer based on the unified strength theory[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2022,26(9):3734-3740. doi: 10.1007/s12205-022-1884-5
[30] 刘明潇,骆亚茹,孙东坡,等. 非定向来流顶冲下生态护坡的抗冲性试验研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版),2023:1-11. (LIU M X,LUO Y R,SUN D P,et al. Experimental study on anti scourability of ecological slope protection under non directional inflow top scour[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University,2023:1-11. (in Chinese) LIU M X, LUO Y R, SUN D P, et al. Experimental study on anti scourability of ecological slope protection under non directional inflow top scour[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2023: 1-11. (in Chinese)
[31] 周云艳. 植物根系固土机理与护坡技术研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学,2010. (ZHOU Y Y. Study on soil consolidation mechanism of plant roots and slope protection technology[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences,2010. (in Chinese) ZHOU Y Y. Study on soil consolidation mechanism of plant roots and slope protection technology[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2010. (in Chinese)
[32] 舒安平,高静,段国胜,等. 基于聚类法的黄河上游沙漠宽谷河段塌岸因子遴选及塌岸程度分级[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2014,54(8):1044-1048. (SHU A P,GAO J,DUAN G S,et al. Cluster analysis for factor classification and riverbank collapse along the desert wide valley reach of the Upper Yellow River[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology),2014,54(8):1044-1048. (in Chinese) SHU A P, GAO J, DUAN G S, et al. Cluster analysis for factor classification and riverbank collapse along the desert wide valley reach of the Upper Yellow River[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2014, 54(8): 1044-1048. (in Chinese)
[33] DAI L,JIA C J,CHEN L,et al. Development characteristics and reactivation mechanism of a large-scale ancient landslide in reservoir area[J]. Applied Sciences,2024,14(7):3107. doi: 10.3390/app14073107
[34] JIA C J,CHEN F L,ZHANG Q,et al. Centrifuge modeling and numerical analysis of reservoir bank landslides triggered by a fast two-step drop in water level[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2023,82(12):465. doi: 10.1007/s10064-023-03490-z
[35] 胡庆,王浩,郭剑波,等. 含水率变化对黄河下游滩岸土体力学性质影响及稳定性分析[J]. 人民黄河,2024,46(2):61-66. (HU Q,WANG H,GUO J B,et al. Influence of water content change to the mechanical properties and stability of beach soil in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River,2024,46(2):61-66. (in Chinese) HU Q, WANG H, GUO J B, et al. Influence of water content change to the mechanical properties and stability of beach soil in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River, 2024, 46(2): 61-66. (in Chinese)
[36] 严建华,张建军,李绪鹏,等. 黄河堤防丁坝(垛)水下根石动态监测预警系统研究[J]. 中国水利,2023(16):64-68. (YAN J H,ZHANG J J,LI X P,et al. Studies on dynamic monitoring and early warning system for underwater root rocks of spur dikes(piers)of the Yellow River[J]. China Water Resources,2023(16):64-68. (in Chinese) YAN J H, ZHANG J J, LI X P, et al. Studies on dynamic monitoring and early warning system for underwater root rocks of spur dikes(piers)of the Yellow River[J]. China Water Resources, 2023(16): 64-68. (in Chinese)
[37] LI Y,LIU Y Q,CHEN J,et al. Advances in retrogressive thaw slump research in permafrost regions[J]. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes,2024,35(2):125-142. doi: 10.1002/ppp.2218
[38] RECKING A,PITON G,MONTABONNET L,et al. Design of fascines for riverbank protection in alpine rivers:insight from flume experiments[J]. Ecological Engineering,2019,138:323-333. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.07.019
[39] 张幸农,牛晨曦,假冬冬,等. 流滑型窝崩水流结构特征及其变化规律[J]. 水科学进展,2020,31(1):112-119. (ZHANG X N,NIU C X,JIA D D,et al. Flow structure characteristics and changes in a simulated riverbank nest-shaped flow slide[J]. Advances in Water Science,2020,31(1):112-119. (in Chinese) ZHANG X N, NIU C X, JIA D D, et al. Flow structure characteristics and changes in a simulated riverbank nest-shaped flow slide[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2020, 31(1): 112-119. (in Chinese)
[40] ZHANG L,ZHOU J W,ZHANG B,et al. Numerical investigation on the solid particle erosion in elbow with water-hydrate-solid flow[J]. Science Progress,2020,103(1):36850419897245.
[41] ZHAO K,GONG Z,ZHANG K L,et al. Laboratory experiments of bank collapse:the role of bank height and near-bank water depth[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Earth Surface),2020,125(5):e2019JF005281. doi: 10.1029/2019JF005281
[42] JAFARNEJAD M,PFISTER M,BRÜHWILER E,et al. Probabilistic failure analysis of riprap as riverbank protection under flood uncertainties[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,2017,31(7):1839-1851. doi: 10.1007/s00477-016-1368-6
[43] 王英珍,夏军强,邓珊珊,等. 黄河下游河道滩岸崩退与淤长过程的耦合模拟[J]. 工程科学与技术,2023,55(4):130-141. (WANG Y Z,XIA J Q,DENG S S,et al. Coupled modelling of bank erosion and accretion in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2023,55(4):130-141. (in Chinese) WANG Y Z, XIA J Q, DENG S S, et al. Coupled modelling of bank erosion and accretion in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2023, 55(4): 130-141. (in Chinese)
[44] 张伊婧,璩向宁,王磊,等. 1987—2022年黄河银川平原段河道演变特征及影响因素[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2024,38(3):92-103. (ZHANG Y J,QU X N,WANG L,et al. Evolution characteristics of the river course within Yinchuan Plain section of the Yellow River,from 1987 to 2022[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2024,38(3):92-103. (in Chinese) ZHANG Y J, QU X N, WANG L, et al. Evolution characteristics of the river course within Yinchuan Plain section of the Yellow River, from 1987 to 2022[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2024, 38(3): 92-103. (in Chinese)
[45] GOTTARDI G,GRAGNANO C G,RANALLI M,et al. Reliability analysis of riverbank stability accounting for the intrinsic variability of unsaturated soil parameters[J]. Structural Safety,2020,86:101973. doi: 10.1016/j.strusafe.2020.101973
[46] YANG Z,MOU X Y,JI H L,et al. Effects of freeze–thaw on bank soil mechanical properties and bank stability[J]. Scientific Reports,2024,14:9808. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60698-z
[47] 谭瑞琪,谢亚军,李欣然,等. 植被防护岸坡加筋机理研究[J]. 中国水运,2023(6):71-74. (TAN R Q,XIE Y J,LI X R,et al. Research on the reinforcement mechanism of vegetation protection bank slope[J]. China Water Transport,2023(6):71-74. (in Chinese) TAN R Q, XIE Y J, LI X R, et al. Research on the reinforcement mechanism of vegetation protection bank slope[J]. China Water Transport, 2023(6): 71-74. (in Chinese)
[48] ZHOU Y Y,WANG X M. Mesomechanics characteristics of soil reinforcement by plant roots[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2019,78(5):3719-3728. doi: 10.1007/s10064-018-1370-y
[49] 甘磊,陈官运,沈振中,等. 堤坝混凝土防渗墙渗透溶蚀演化规律研究[J]. 水利学报,2022,53(8):939-948. (GAN L,CHEN G Y,SHEN Z Z,et al. Evolution law of leakage dissolution of concrete cutoff wall of embankments[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2022,53(8):939-948. (in Chinese) GAN L, CHEN G Y, SHEN Z Z, et al. Evolution law of leakage dissolution of concrete cutoff wall of embankments[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2022, 53(8): 939-948. (in Chinese)
[50] 娄森元. 黄河宁夏段河道治理工程设计[J]. 人民长江,2024,55(S1):121-124. (LOU S Y. Design of Yellow River Ningxia section river management project[J]. Yangtze River,2024,55(S1):121-124. (in Chinese) LOU S Y. Design of Yellow River Ningxia section river management project[J]. Yangtze River, 2024, 55(S1): 121-124. (in Chinese)
[51] 程亦菲,夏军强,周美蓉,等. 黄河下游不同河段分组悬沙输移对河床冲淤的影响[J]. 水科学进展,2022,33(3):506-517. (CHENG Y F,XIA J Q,ZHOU M R,et al. Effects of grouped suspended sediment transport on channel evolution in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science,2022,33(3):506-517. (in Chinese) CHENG Y F, XIA J Q, ZHOU M R, et al. Effects of grouped suspended sediment transport on channel evolution in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2022, 33(3): 506-517. (in Chinese)
[52] ADHIKARI A R,GAUTAM M R,YU Z B,et al. Estimation of root cohesion for desert shrub species in the Lower Colorado riparian ecosystem and its potential for streambank stabilization[J]. Ecological Engineering,2013,51:33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.12.005
[53] 王紫荆,徐梦珍,胡宏昌,等. 1982—2020年黄河流域植被变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 水科学进展,2023,34(4):499-509. (WANG Z J,XU M Z,HU H C,et al. Characteristics of vegetation changes and their drivers in the Yellow River basin from 1982 to 2020[J]. Advances in Water Science,2023,34(4):499-509. (in Chinese) WANG Z J, XU M Z, HU H C, et al. Characteristics of vegetation changes and their drivers in the Yellow River basin from 1982 to 2020[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2023, 34(4): 499-509. (in Chinese)
[54] ZHANG M,HU D D,FAN J. Study on the application of vegetation protection and ecological restoration technology in stone slope[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2020,510(4):042024. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/510/4/042024
[55] 赵文婷,姜晓晗,李萌萌,等. 黄丘区自然植被对暴雨的拦蓄作用:以坊塌小流域为例[J]. 水科学进展,2023,34(5):731-743. (ZHAO W T,JIANG X H,LI M M,et al. Interception and storage of heavy rainfall by natural vegetations in the loess hilly and gully area[J]. Advances in Water Science,2023,34(5):731-743. (in Chinese) ZHAO W T, JIANG X H, LI M M, et al. Interception and storage of heavy rainfall by natural vegetations in the loess hilly and gully area[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2023, 34(5): 731-743. (in Chinese)
[56] 宗全利,张禹洋,唐瑞泽,等. 塔里木河植被根系对河岸冲刷特性影响的现场试验[J]. 水科学进展,2024,35(2):232-243. (ZONG Q L,ZHANG Y Y,TANG R Z,et al. Field experiment on the influence of vegetation roots on riverbank erosion characteristics in the Tarim River[J]. Advances in Water Science,2024,35(2):232-243. (in Chinese) ZONG Q L, ZHANG Y Y, TANG R Z, et al. Field experiment on the influence of vegetation roots on riverbank erosion characteristics in the Tarim River[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2024, 35(2): 232-243. (in Chinese)
[57] 吴洁,张静,付江涛. 水利工程堤坝护坡植被修复技术与方法研究:评《水电工程陡边坡植被混凝土生态修复技术规范》[J]. 人民黄河,2024,46(4):I0006. (WU J,ZHANG J,FU J T. Study on vegetation restoration technology and method of dam slope protection in hydraulic engineering:comment on technical specification for ecological restoration of vegetation concrete on steep slope of hydropower engineering[J]. Yellow River,2024,46(4):I0006. (in Chinese) WU J, ZHANG J, FU J T. Study on vegetation restoration technology and method of dam slope protection in hydraulic engineering: comment on technical specification for ecological restoration of vegetation concrete on steep slope of hydropower engineering[J]. Yellow River, 2024, 46(4): I0006. (in Chinese)
[58] 易雨君,谢泓毅,宋劼,等. 黄河口盐沼湿地植被群落适宜生境模拟Ⅱ:应用[J]. 水利学报,2021,52(4):401-408. (YI Y J,XIE H Y,SONG J,et al. Simulation of salt marsh vegetation community's suitable habitat in Yellow River Estuary Ⅱ:application[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2021,52(4):401-408. (in Chinese) YI Y J, XIE H Y, SONG J, et al. Simulation of salt marsh vegetation community's suitable habitat in Yellow River Estuary Ⅱ: application[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2021, 52(4): 401-408. (in Chinese)
[59] 王科. 黄河下游防洪工程区植被现状调查与评价[D]. 新乡:河南师范大学,2012. (WANG K. Investigation and evaluation of vegetation status in flood control engineering area of the Lower Yellow River[D]. Xinxiang:Henan Normal University,2012. (in Chinese) WANG K. Investigation and evaluation of vegetation status in flood control engineering area of the Lower Yellow River[D]. Xinxiang: Henan Normal University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[60] 晏长根,梁哲瑞,贾卓龙,等. 黄土边坡坡面防护技术综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报,2023,23(4):1-22. (YAN C G,LIANG Z R,JIA Z L,et al. Review on surface protection technologies of loess slope[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2023,23(4):1-22. (in Chinese) YAN C G, LIANG Z R, JIA Z L, et al. Review on surface protection technologies of loess slope[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(4): 1-22. (in Chinese)
[61] 徐志平,贾卓龙,晏长根,等. 聚丙烯纤维加筋黄土边坡防护原位测试及改进策略[J]. 人民黄河,2024,46(4):111-116. (XU Z P,JIA Z L,YAN C G,et al. In situ test and improvement measures of polypropylene fiber-reinforced loess slope protection[J]. Yellow River,2024,46(4):111-116. (in Chinese) XU Z P, JIA Z L, YAN C G, et al. In situ test and improvement measures of polypropylene fiber-reinforced loess slope protection[J]. Yellow River, 2024, 46(4): 111-116. (in Chinese)
[62] 张旭. 黄河下游堤防生态护坡措施试验与效果评价[D]. 济南:济南大学,2022. (ZHANG X. Experiment and effect evaluation of ecological slope protection measures for dikes in the Lower Yellow River[D]. Jinan:University of Jinan,2022. (in Chinese) ZHANG X. Experiment and effect evaluation of ecological slope protection measures for dikes in the Lower Yellow River[D]. Jinan: University of Jinan, 2022. (in Chinese)
[63] 焦锡昆. 植生混凝土狗牙根草的适生性及护坡效果研究[D]. 济南:济南大学,2023. (JIAO X K. Research on the suitability and slope protection effect of eco-plant concrete cynodon dactylon[D]. Jinan:Jinan University,2023. (in Chinese) JIAO X K. Research on the suitability and slope protection effect of eco-plant concrete cynodon dactylon[D]. Jinan: Jinan University, 2023. (in Chinese)
[64] 孟祥文. 黄河河道工程坍塌险情处置及扭王(工)体抢险应用探究[J]. 人民黄河,2024,46(S1):13-14. (MENG X W. A stability analysis of different stack types of accropode[J]. Yellow River,2024,46(S1):13-14. (in Chinese) MENG X W. A stability analysis of different stack types of accropode[J]. Yellow River, 2024, 46(S1): 13-14. (in Chinese)
[65] 王国强,苏乃华,董继坤. 黄河下游河道整治工程根石稳定性分析[J]. 人民黄河,2024,46(S1):19-20. (WANG G Q,SU N H,DONG J K. Stability analysis of root stones in the Yellow River downstream channel improvement project[J]. Yellow River,2024,46(S1):19-20. (in Chinese) WANG G Q, SU N H, DONG J K. Stability analysis of root stones in the Yellow River downstream channel improvement project[J]. Yellow River, 2024, 46(S1): 19-20. (in Chinese)
[66] 王先昌,韩继荣,王瑞. 引黄灌区渠道护坡改造方案分析[J]. 海河水利,2023(8):32-35. (WANG X C,HAN J R,WANG R. Analysis of slope protection renovation plan for channels in the Yellow River Irrigation Area[J]. Haihe River Conservancy,2023(8):32-35. (in Chinese) WANG X C, HAN J R, WANG R. Analysis of slope protection renovation plan for channels in the Yellow River Irrigation Area[J]. Haihe River Conservancy, 2023(8): 32-35. (in Chinese)
[67] 包家全,樊好河,罗延婷,等. 黄河下游控导土工枕布护坡抢险关键技术研究[J]. 人民黄河,2022,44(11):48-52. (BAO J Q,FAN H H,LUO Y T,et al. Study on the key technology for emergency rescue by using geotechnical fabric for slope protection of controlled and guided engineering in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River,2022,44(11):48-52. (in Chinese) BAO J Q, FAN H H, LUO Y T, et al. Study on the key technology for emergency rescue by using geotechnical fabric for slope protection of controlled and guided engineering in the Lower Yellow River[J]. Yellow River, 2022, 44(11): 48-52. (in Chinese)
[68] 潘志豪,王东武,刘学应,等. 水利工程中生态护岸型式研究综述[J]. 浙江水利水电学院学报,2023,35(2):25-31. (PAN Z H,WANG D W,LIU X Y,et al. Research review on ecological revetment types in hydraulic engineering[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Water Resources and Electric Power,2023,35(2):25-31. (in Chinese) PAN Z H, WANG D W, LIU X Y, et al. Research review on ecological revetment types in hydraulic engineering[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2023, 35(2): 25-31. (in Chinese)
[69] ROSGEN D L. A practical method of computing streambank erosion rate[C]//Proceedings of the Seventh Federal Interagency Sedimentation Conference. Reno, NV:Subcommittee on Sedimentation, 2001.
[70] LARSEN E W,PREMIER A K,GRECO S E. Cumulative effective stream power and bank erosion on the Sacramento River,California,USA[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association,2006,42(4):1077-1097. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.2006.tb04515.x
[71] NEWTON S E,DRENTEN D M. Modifying the Bank Erosion Hazard Index (BEHI) protocol for rapid assessment of streambank erosion in Northeastern Ohio[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments,2015(96):52330.
[72] MCMILLAN M,LIEBENS J,METCALF C. Evaluating the BANCS streambank erosion framework on the northern gulf of Mexico coastal plain[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association,2017,53(6):1393-1408. doi: 10.1111/1752-1688.12572
[73] 王延贵,齐梅兰,金亚昆. 河道岸滩稳定性综合评价方法[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2016,36(5):55-59. (WANG Y G,QI M L,JIN Y K. Comprehensive evaluation method for river bank stability[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources,2016,36(5):55-59. (in Chinese) WANG Y G, QI M L, JIN Y K. Comprehensive evaluation method for river bank stability[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2016, 36(5): 55-59. (in Chinese)
[74] 王延贵. 冲积河流岸滩崩塌机理的理论分析及试验研究[D]. 北京:中国水利水电科学研究院,2003. (WANG Y G. Theoretical analysis and experimental study on the mechanism of beach collapse in alluvial rivers[D]. Beijing:China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research,2003. (in Chinese) WANG Y G. Theoretical analysis and experimental study on the mechanism of beach collapse in alluvial rivers[D]. Beijing: China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2003. (in Chinese)
[75] KLAVON K,FOX G,GUERTAULT L,et al. Evaluating a process-based model for use in streambank stabilization:insights on the Bank Stability and Toe Erosion Model (BSTEM)[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2017,42(1):191-213. doi: 10.1002/esp.4073
[76] LI Z W,YANG H Y,XIA J Q,et al. Channel morphologic processes of a highly sinuous bend approaching neck cutoff by bank erosion in the Middle Yangtze River[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research,2021,36(4):457-467. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsrc.2021.01.001
[77] 假冬冬,杨俊,郝由之,等. 冻融作用对我国北方季节性冰冻河流岸坡稳定性的影响:以松花江典型河段为例[J]. 湖泊科学,2023,35(3):1072-1081. (JIA D D,YANG J,HAO Y Z,et al. Influence of the freeze-thaw effect on the seasonally frozen riverbank stability:a case study of the typical reach of Songhua River,China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences,2023,35(3):1072-1081. (in Chinese) doi: 10.18307/2023.0325 JIA D D, YANG J, HAO Y Z, et al. Influence of the freeze-thaw effect on the seasonally frozen riverbank stability: a case study of the typical reach of Songhua River, China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2023, 35(3): 1072-1081. (in Chinese) doi: 10.18307/2023.0325
[78] DENG S S,XIA J Q,ZHOU M R,et al. Riparian groundwater level variation and its impacts on bank erosion in the Middle Yangtze River[J]. Water Resources Research,2022,58(7):e2022WR032354. doi: 10.1029/2022WR032354
[79] 张旭,陈静,黄波. 黄河下游堤防生态护坡试验与效果评价[J]. 人民黄河,2021,43(6):46-49,54. (ZHANG X,CHEN J,HUANG B. Experiment and effect evaluation of Eco-Protection slope on Yellow River downstream dike[J]. Yellow River,2021,43(6):46-49,54. (in Chinese) ZHANG X, CHEN J, HUANG B. Experiment and effect evaluation of Eco-Protection slope on Yellow River downstream dike[J]. Yellow River, 2021, 43(6): 46-49, 54. (in Chinese)
[80] GAO L,XU X Z,XIA J Q. Deciphering the role of riverbank collapse in the braided reach of the Lower Yellow River:helpful or harmful?[J]. Journal of Earth System Science,2024,133(1):30. doi: 10.1007/s12040-023-02240-9
[81] 张俊飞,潘磊,刘嘉森. 黄河下游马渡险工28护岸、29坝较大险情出险原因分析[J]. 人民黄河,2022,44(S1):12-13. (ZHANG J F,PAN L,LIU J S. Development and application of the Yellow River flood control decision support system at the grass-roots level[J]. Yellow River,2022,44(S1):12-13. (in Chinese) ZHANG J F, PAN L, LIU J S. Development and application of the Yellow River flood control decision support system at the grass-roots level[J]. Yellow River, 2022, 44(S1): 12-13. (in Chinese)
[82] 杨李. 基于无人机倾斜摄影的河岸护坡损害动态监测方法[J]. 广州航海学院学报,2023,31(2):70-73. (YANG L. Dynamic monitoring method of bank slope protection damage based on UAV tilt photography[J]. Journal of Guangzhou Maritime University,2023,31(2):70-73. (in Chinese) YANG L. Dynamic monitoring method of bank slope protection damage based on UAV tilt photography[J]. Journal of Guangzhou Maritime University, 2023, 31(2): 70-73. (in Chinese)
[83] 张磊. 基于DFOS的库岸边坡变形机理及预测研究[D]. 南京:南京大学,2020. (ZHANG L. Research on deformation mechanism and prediction of reservoir bank slope based on DFOS[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing University,2020. (in Chinese) ZHANG L. Research on deformation mechanism and prediction of reservoir bank slope based on DFOS[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2020. (in Chinese)
[84] PINTO A A S,FERNANDES L F S,de OLIVEIRA MAIA R J F. A method for selecting suitable technical solutions to support sustainable riverbank stabilization[J]. Area,2019,51(2):285-298. doi: 10.1111/area.12488
[85] 李国权,马冰,孙红义,等. 应急处置(抢险救灾)工程河道岸坡塌岸分析及其防治[J]. 人民黄河,2023,45(S1):9-10. (LI G Q,MA B,SUN H Y,et al. Bank-failure types of typical mountain-river reservoirs[J]. Yellow River,2023,45(S1):9-10. (in Chinese) LI G Q, MA B, SUN H Y, et al. Bank-failure types of typical mountain-river reservoirs[J]. Yellow River, 2023, 45(S1): 9-10. (in Chinese)
[86] 费晓昕,张幸农. 平顺抛石护岸水毁速率试验研究[J]. 人民长江,2021,52(11):207-211. (FEI X X,ZHANG X N. Experimental study on water damage rate of smooth riprap revetment[J]. Yangtze River,2021,52(11):207-211. (in Chinese) FEI X X, ZHANG X N. Experimental study on water damage rate of smooth riprap revetment[J]. Yangtze River, 2021, 52(11): 207-211. (in Chinese)
[87] 郑帅. 黄河干流上游段防洪工程护岸及护坡技术方案探究[J]. 东北水利水电,2022,40(9):1-4,43. (ZHENG S. Study on the technical scheme of bank protection and slope protection for flood control works in the upper reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Water Resources & Hydropower of Northeast China,2022,40(9):1-4,43. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0624.2022.9.dbslsd202209001 ZHENG S. Study on the technical scheme of bank protection and slope protection for flood control works in the upper reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Water Resources & Hydropower of Northeast China, 2022, 40(9): 1-4, 43. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0624.2022.9.dbslsd202209001
[88] 王开荣,王崇浩,杜小康,等. 黄河口泥沙的治理实践与评价[J]. 泥沙研究,2024,49(2):72-80. (WANG K R,WANG C H,DU X K,et al. Practice and evaluation of sediment control in the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research,2024,49(2):72-80. (in Chinese) WANG K R, WANG C H, DU X K, et al. Practice and evaluation of sediment control in the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2024, 49(2): 72-80. (in Chinese)
[89] MAXWALD M,CROCETTI C,FERRARI R,et al. Soil and water bioengineering applications in Central and South America:a transferability analysis[J]. Sustainability,2020,12(24):10505. doi: 10.3390/su122410505
[90] 张同鑫,潘毅,张壮,等. 加筋生态护坡技术的应用与发展[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2017(6):110-117. (ZHANG T X,PAN Y,ZHANG Z,et al. Application and development of TRM technology in revetment works[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering,2017(6):110-117. (in Chinese) ZHANG T X, PAN Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Application and development of TRM technology in revetment works[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2017(6): 110-117. (in Chinese)
[91] 李昂,秦钏芮. 水利水电工程扰动区生态护坡技术比较研究[J]. 水利水电快报,2024,45(2):115-121. (LI A,QIN C R. Comparative study of ecological slope protection technology in vegetation degradation areas disturbed by water conservancy projects[J]. Express Water Resources & Hydropower Information,2024,45(2):115-121. (in Chinese) LI A, QIN C R. Comparative study of ecological slope protection technology in vegetation degradation areas disturbed by water conservancy projects[J]. Express Water Resources & Hydropower Information, 2024, 45(2): 115-121. (in Chinese)
[92] 刘滨,杨德生,张淑红,等. 抛投防汛石沿坡面滑滚落距影响因素研究[J]. 人民黄河,2024,46(8):60-64,70. (LIU B,YANG D S,ZHANG S H,et al. Study on the influencing factors of drop distance of flood control stone sliding and rolling along the slope during throwing[J]. Yellow River,2024,46(8):60-64,70. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2024.08.011 LIU B, YANG D S, ZHANG S H, et al. Study on the influencing factors of drop distance of flood control stone sliding and rolling along the slope during throwing[J]. Yellow River, 2024, 46(8): 60-64, 70. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2024.08.011
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 秦梦春,白玉川,徐海珏,刘军政,白洋. 黄河下游游荡段畸形河势的时空分布及演变规律. 水科学进展. 2025(01): 62-75 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: