Pore-scale simulations of fluid flow and solute transport in porous media by high-performance Lattice Boltzmann Method
-
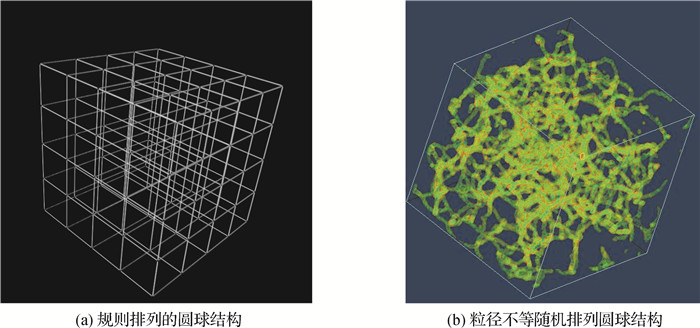
摘要: 深入探究孔隙尺度下的流体流动特性和溶质运移规律对石油开采、农田养分管理、地下水污染修复有着重要意义。以人工构建的多孔介质结构和同步辐射X射线显微CT扫描的土壤团聚体(分辨率3.7 μm)为研究对象,在空间节点数多达64 000 000的情况下,基于格子Boltzmann模型和GPU并行技术计算得到多孔介质流体运动和溶质运移过程的关键参数,并据此探究多孔介质空间异质性对水力学特性的影响。通过对3组不同结构的多孔介质比较发现,结构复杂程度最高的土壤样品和不规则堆叠的圆球结构的渗透率在100 mD(即10-13m2)量级,远低于规则堆叠的圆球结构(>20 000 mD);土壤的迂曲度为1.40~1.60,明显高于规则堆叠的圆球结构。研究结果表明,渗透率大的样品具有较小的迂曲度,这与结构的空间异质性有较强的关系;土壤的渗透率和迂曲度呈现各向异性;在水力梯度一定的前提下,渗透率较大的样品,纵向弥散系数也较大;同时,结构的异质性也会影响溶质的穿透曲线。本研究提出的模拟方法可在土壤结构中进行高效的水流运动和溶质运移模拟,可用于土壤多孔介质在孔隙尺度下的水力学特性研究。
-
关键词:
- 孔隙尺度 /
- 格子Boltzmann法 /
- 流体流动 /
- 溶质运移
Abstract: Understanding the mechanism of fluid flow and solute transport at the pore scale is of great importance for oil recovery, crop nutrient management and groundwater pollution restoration. This study employed lattice Boltzmann model combining with GPU parallel technology to investigate the porous media of computer-generated structures and synchrotron-based X-ray micro-CT scans of soil aggregates (resolution 3.7 μm). The key parameters of fluid flow and solute transport in the porous media were obtained, and the influence of spatial heterogeneity of porous media on hydraulic properties was explored by high-performance simulation (spatial nodes up to 64 000 000). By comparing the three groups of porous media with different structures, it was found that the permeabilities of the soil sample with the highest structural complexity and beads irregularly stacked are on the order of 100 mD (i.e. 10-13m2), which is much lower than that of the regularly stacked beads (>20 000 mD); The soil sample has a tortuosity of 1.40~1.60, which is significantly higher than that of the regularly stacked beads. Our results show that the porous media with high permeabilities have small degree of tortuosity, indicating that the permeabilities of porous media are related to the spatial heterogeneity of the structure. The permeability and tortuosity of soil aggregate are anisotropic. At given pressure gradient, the longitudinal diffusion coefficient is greater for a sample with higher permeability. The heterogeneity of the pore structure also affects the breakthrough curve. The method established in this work can simulate water flow and solute migration in real soil structure, and can be used to study the hydraulic characteristics of porous media at the pore scale.-
Keywords:
- pore-scale modeling /
- Lattice Boltzmann Method /
- fluid flow /
- solute transport
-
-
表 1 多孔介质的基本信息
Table 1 Physical properties of porous structure
样品序号 计算区域 真实大小/mm3 总孔隙度/% Sphere300 300×300×300 1.11×1.11×1.11 47.61 Sphere160 160×160×160 0.592×0.592×0.592 47.89 Isphere160 160×160×160 0.592×0.592×0.592 16.48 Soil400 400×400×400 1.48×1.48×1.48 31.12 表 2 多孔介质的水力学特性
Table 2 Hydraulic properties of porous structure
样品序号 kx/mD ky/mD kz/mD Tx Ty Tz DL/Dm Sphere300 28 772 28 772 28 772 1.02 1.02 1.02 0.696 8 Sphere160 25 188 25 188 25 188 1.03 1.03 1.03 0.656 1 Isphere160 261 782 936 1.66 1.45 1.41 0.397 8 Soil400 696 854 604 1.46 1.40 1.59 0.234 3 注:渗透率单位mD为毫达西, 1mD=10-15 m2。 表 3 GPU并行的加速效果
Table 3 Effect of GPU parallel computation
样品序号 孔隙节点数 CPU时间(tCPU)/h GPU时间(tGPU)/min tCPU/tGPU Sphere160 1 961 750 50.70 9.57 318 Isphere160 675 041 27.96 6.67 252 Soil400 19 914 848 29.59 56.05 32 注:Sphere160和Isphere160计算条件为CPU(i5-7300, 2.50 GHz)和计算显卡NVIDIA GeForce GTX TITAN X(GM200, 1 000 MHz);Soil 400计算条件为双CPU(Intel Xeon E5-2680 2.8 GHz)和GPU集群, 4张NIVIDIA Tesla K20M(频率500 MHz, 核心数2 496个)。 -
[1] NING Y, JIANG Y, LIU H L, et al. Numerical modeling of slippage and adsorption effects on gas transport in shale formations using the lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 26: 345-355. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.06.015
[2] 姚军, 赵建林, 张敏, 等.基于格子Boltzmann方法的页岩气微观流动模拟[J].石油学报, 2015, 36(10): 1280-1289. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201510011 YAO J, ZHAO J L, ZHANG M, et al. Microscale shale gas flow simulation based on Lattice Boltzmann Method[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(10): 1280-1289. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201510011
[3] XU H, DANG Z. Lattice Boltzmann modeling of carbon deposition in porous anode of a solid oxide fuel cell with internal reforming[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 178: 294-307. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.06.007
[4] KANG Q J, CHEN L, VALOCCHI A J, et al. Pore-scale study of dissolution-induced changes in permeability and porosity of porous media[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 517: 1049-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.06.045
[5] ZHANG X X, CRAWFORD J W, FLAVEL R J, et al. A multi-scale Lattice Boltzmann model for simulating solute transport in 3-D X-ray micro-tomography images of aggregated porous materials[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 541: 1020-1029. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.08.013
[6] 康学远, 施小清, 邓亚平, 等.基于EnKF融合地球物理数据刻画含水层非均质性[J].水科学进展, 2018, 29(1): 40-49. http://journal16.magtechjournal.com/Jweb_skxjz/CN/abstract/abstract2795.shtml KANG X Y, SHI X Q, DENG Y P, et al. Assimilation of hydrogeophysical data for the characterization of subsurface heterogeneity using Ensemble Kalman Filter (EnKF)[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(1): 679-684. (in Chinese) http://journal16.magtechjournal.com/Jweb_skxjz/CN/abstract/abstract2795.shtml
[7] 周昊, 芮淼, 岑可法.多孔介质内流体流动的大涡格子Boltzmann方法研究[J].浙江大学学报(工学版), 2012, 46(9): 1660-1665. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2012.09.017 ZHOU H, RUI M, CEN K F. Study of flow in porous media by LES-LBM coupling method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2012, 46(9): 1660-1665. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2012.09.017
[8] 蒋昌波, 刘洋, 邓斌, 等.出渗对均匀大粒径泥沙附近水动力特性影响[J].水科学进展, 2017, 28(1): 67-75. http://journal16.magtechjournal.com/Jweb_skxjz/CN/abstract/abstract2694.shtml JIANG C B, LIU Y, DENG B, et al. Effect of upward seepage on hydrodynamic characteristics around uniform coarse grains[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2017, 28(1): 67-75. (in Chinese) http://journal16.magtechjournal.com/Jweb_skxjz/CN/abstract/abstract2694.shtml
[9] AHRENHOLZ B, TOLKE J, LEHMANN P, et al. Prediction of capillary hysteresis in a porous material using lattice-Boltzmann methods and comparison to experimental data and a morphological pore network model[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2008, 31(9): 1151-1173. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2008.03.009
[10] MEHMANI Y, BALHOFF M T. Mesoscale and hybrid models of fluid flow and solute transport[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2015, 80(1): 433-459. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2015.80.13
[11] VOGEL H J, TOLKE J, SCHULZ V P, et al. Comparison of a Lattice-Boltzmann model, a full-morphology model, and a pore network model for determining capillary pressure-saturation relationships[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2005, 4(2): 380-388. doi: 10.2136/vzj2004.0114
[12] 徐鹏, 李翠红, 柳海成, 等.多尺度多孔介质有效气体输运参数的分形特征[J].中国地质大学学报, 2017, 42(8): 1373-1378. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201708015 XU P, LI C H, LIU H C, et al. Fractal features of the effective gas transport coefficient for multiscale porous media[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2017, 42(8): 1373-1378. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201708015
[13] CHEN S Y, CHEN H D, MARTNEZ D, et al. Lattice Boltzmann model for simulation of magnetohydrodynamics[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1991, 67(27): 3776. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.67.3776
[14] 何雅玲, 王勇, 李庆.格子Boltzmann方法的理论及应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2009. HE Y L, WANG Y, LI Q. Lattice Boltzmann method: theory and applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[15] CHEN C, HU D D, MARTYSEVICH V N. Applications of high-resolution imaging and high-performance parallel computing in unconventional energy recovery[C]//Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference. Abu Dhabi: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2014.
[16] PAN C X, LUO L S, MILLER C T. An evaluation of lattice Boltzmann schemes for porous medium flow simulation[J]. Computers & fluids, 2006, 35(8): 898-909. doi: 10.1016-j.compfluid.2005.03.008/
[17] ZHOU H X, YU X L, CHEN C, et al. Evaluating hydraulic properties of biochar-amended soil aggregates by high-performance pore-scale simulations[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2018, 82(1): 1-9. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2017.02.0053
[18] CHEN C, LAU B L T, GAILLARD J F, et al. Temporal evolution of pore geometry, fluid flow, and solute transport resulting from colloid deposition[J]. Water Resources Research, 2009, 45(6): W06416.1-W06416.12. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1029/2008WR007252
[19] BHATNAGAR P L, GROSS E P, KROOK M. A model for collision processes in gases: I: small amplitude processes in charged and neutral one-component systems[J]. Physical Review, 1954, 94(3): 511. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.94.511
[20] 杨艳霞, 李静. 3-D格子Boltzmann传质模型模拟生物膜降解有机污水[J].农业工程学报, 2018, 34(10): 225-230. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.10.028 YANG Y X, LI J. Simulation of biomembrane degrading organic wastewater by 3-D lattice Boltzmann mass transfer model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(10): 225-230. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.10.028
[21] TAKAJI I, MASATO Y, OGINO F. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of flows in a three-dimensional porous structure[J]. International Journal for Numerical Mehods in Fluids, 1999, 29: 737-748. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0363(19990415)29:7<737::AID-FLD813>3.0.CO;2-H
[22] INAMURO T, YOSHINO M, OGINO F. Accuracy of the lattice Boltzmann method for small Knudsen number with finite Reynolds number[J]. Physics of Fluids, 1997, 9(11): 3535-3542. doi: 10.1063/1.869426
[23] THOMPSON P A. Compressible-fluid dynamic[M]. New York:McGraw-Hill, 1971.
[24] MULJADI B P, BLUNT M J, RAEINI A Q, et al. The impact of porous media heterogeneity on non-Darcy flow behaviour from pore-scale simulation[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2015.[doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.05.019]
[25] CHEN C, PACKMAN A I, GAILLARD J F. Pore-scale analysis of permeability reduction resulting from colloid deposition[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35: L07404. doi: 10.1029-2007GL033077/
[26] 蔡勇, 李光耀, 王琥. GPU通用计算平台上中心差分格式显式有限元并行计算[J].计算机研究与发展, 2013, 50(2): 412-419. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyjyfz201302021 CAI Y, LI G Y, WANG H. Parallel computing of central difference explicit finite element based on GPU general computing platform[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2013, 50(2): 412-419. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyjyfz201302021
[27] THORNE D T. Lattice Boltzmann modeling: an introduction for geoscientists and engineers[M]. Berlin:Springer, 2006.
[28] 施小清, 吴吉春, 袁永生, 等.含水介质各向异性对渗透系数空间变异性统计的影响[J].水科学进展, 2005, 16(5): 679-684. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2005.05.011 SHI X Q, WU J C, YUAN Y S, et al. Effect of the anisotropy in porous media on the spatial variability of the hydraulic conductivity[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2005, 16(5): 679-684. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2005.05.011
[29] 周志芳, 庄超, 戴云峰, 等.单孔振荡式微水试验确定裂隙岩体各向异性渗透参数[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(2): 271-278. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb201502006 ZHOU Z F, ZHUANG C, DAI Y F, et al. Determing anisotropic hydraulic conductivity in fractured rocks based on single-borehole slug tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(2): 271-278. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb201502006
[30] 夏源, 吴吉春, 张勇.改进时间分数阶模型模拟非Fick溶质运移[J].水科学进展, 2013, 24(3): 349-357. http://journal16.magtechjournal.com/Jweb_skxjz/CN/abstract/abstract2297.shtml XIA Y, WU J C, ZHANG Y. Tempered time-fractional advection-dispersion equation for modeling non-Fickian transport[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2013, 24(3): 349-357. (in Chinese) http://journal16.magtechjournal.com/Jweb_skxjz/CN/abstract/abstract2297.shtml
[31] ZHANG X X, LYU M C. Persistence of anomalous dispersion in uniform porous media demonstrated by pore-scale simulations[J]. Water Resources Research, 2007, 43(7).[doi: 10.1029/2006WR005557]
[32] HOU Y S, JIANG J G, WU J C. Anomalous solute transport in cemented porous media: pore-scale simulations[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2018.[doi: 10.2136/sssaj2017.04.0125]





 下载:
下载: